Based on the Publication Manual of the America Psychological Association (6th edition)
General formatting (see Figure 2.1 p. 41 for an example)
- Times Roman typeface size 12 double-spaced
- Margins – 1 inch
- Page numbers – plain numbers, top right corner
- Header – top left corner
- On title page: ‘Running head: [SHORTENED TITLE IN CAPS]’
- On all subsequent pages: ‘[SHORTENED TITLE IN CAPS]’
Levels of Headings ( Table 3.1, p. 62; see Figure 2.1, pp. 44-45 for an example
Organization
Title page (see Figure 2.1 p. 41 for an example) includes:
- Title of writing piece
- Author’s name (replace with student ID for anonymous marking)
- Author’s institutional affiliation (e.g. School of Psychology, Bangor University)
- Some modules require additional information (e.g. module code, graduate instructor’s name) so check assignment guidelines
Research reports (see Chapter 2, p.21 for a detailed description of each section) include:
- Abstract*
- Introduction* (starts on new page)
- Methods* (includes subsections e.g. *participants, materials/apparatus, *design, *procedures, data analysis)
- Results*
- Discussion*
- Conclusion
- Appendix/Appendices (if multiple appendices are included, differentiate between them using capital letters; e.g. Appendix A, Appendix B etc.)
* = compulsory
Tables/Figures
Number all tables/figures with Arabic numerals in the order in which they are first mentioned in the text (e.g. Figure 1, not Figure 1a, Table 2b); if included in appendix, use both the capital letter corresponding to the appendix and numerals (e.g. Table A1 is the first table in Appendix A).
Table Layout (see Table 5.1 p 129 for an explanation of the basic components of a table; see Section 5.18 pp. 141-149 for examples of standard tables for presenting several types of data; see section 5.19 p. 150 for a table checklist)
- Caption – positioned above the table; table title (but not table number) in Italics
- Cell Margins:
- For columns – not used
- For rows – used to separate column headings from the data

Figures (see Table 5.1 p 129 for an explanation of the basic components of a table; see Section 5.22 pp. 152-160 for examples of figures; see section 5.30 p. 167 for a figure checklist)
- Caption – positioned immediately below the figure; figure number (but not figure title) in Italics
- Graph axes should be clearly labelled
- Elements (e.g. of diagrams/charts) within the figure should be labelled or explained in the caption
- Units of measurements should be provided

Crediting Sources
In-text citations (see pp. 174-179 for a detailed explanation)
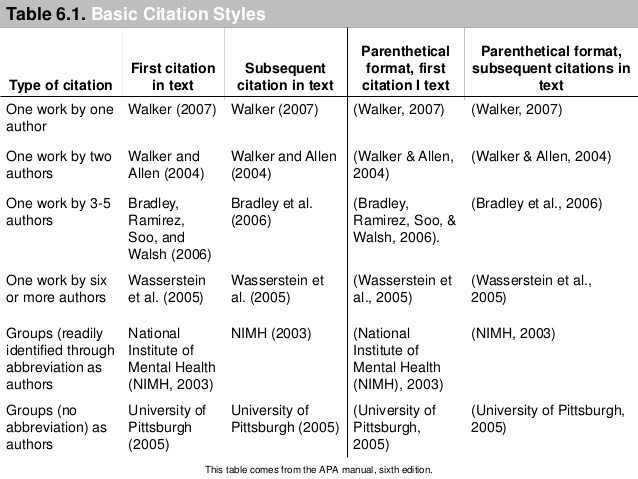
Reference list (see pp. 180-192 for a detailed explanation, see Chapter 7 p.193 for examples by type of source)
General formatting
- Title ‘References’
- References listed in alphabetical order (see section 6.25 foe a detailed explanation of ordering in different situations)
- Hanging indent
Referencing a book (Section 7.02, p.202)
Author, A. A., & Author, B. B. (year of publication). Title. City, Country (or state for USA): Publisher.
E.g.:
Thomas, K. (1962). The structure of scientific revolutions. Chicago, IL: University of Chicago Press.
Referencing a journal article (Section 7.01, p.198)
Author, A. A., Author, B. B., & Author, C. C. (year of publication). Title of article. Title of Journal, volume number(issue number), pp-pp. doi:xx.xxxxxxx
E.g.:
Binney, R. J., Parker, G. J., & Lambon Ralph, M. A. (2012). Convergent connectivity and graded specialization in the rostral human temporal lobe as revealed by diffusion-weighted imaging probabilistic tractography. Journal of cognitive neuroscience, 24(10), 1998-2014. doi: 10.1162/jocn_a_00263
Reducing bias in language (see Sections 3.12-3.17 pp.73-77 for a detailed explanation by topic)
Avoid term -> preferred term(s)
- Subjects -> participants
- Transgender (noun) -> transgender (adjective) e.g. female-to-male transgender individuals/ transsexual (noun/adjective)
- Sex change -> sex-reassignment
- Sexual preference -> sexual orientation
- Homosexual -> lesbians, gay man, bisexual men/women
- Under 18 years -> girl/boy (<12 years old), young man/women or adolescents (13-17 years old), 18 years old or older – women/man/adults
- Elderly/senior (noun) -> elderly/senior (adjective), older adults
Disabilities
- avoid language that objectifies a person by their condition (e.g. autistic, neurotic), that uses pictorial metaphors (e.g. confined to a wheelchair), that uses excessive and negative labels (e.g. AIDS victim, brain damaged)
- use people-first language, and do not focus on the individual’s disabling or chronic condition (e.g. person with paraplegia, youth diagnosed with autism, individuals with intellectual disabilities)